P0420 Code Explained: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) – Causes & Fixes
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. See our affiliate disclaimer for more information.
What does the P0420 Catalyst Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) mean?

P0420 code gets triggered when the Engine Control Module detects a condition that indicates that the catalytic converter is operating below the minimum allowable efficiency threshold.
The purpose of a catalytic converter is to use a chamber called a catalyst to change the harmful compounds from an engine’s emissions into environmentally safe gases.
When the engine releases harmful gases like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons, these gases travel through the catalyst and are converted into safer gases like steam, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen.
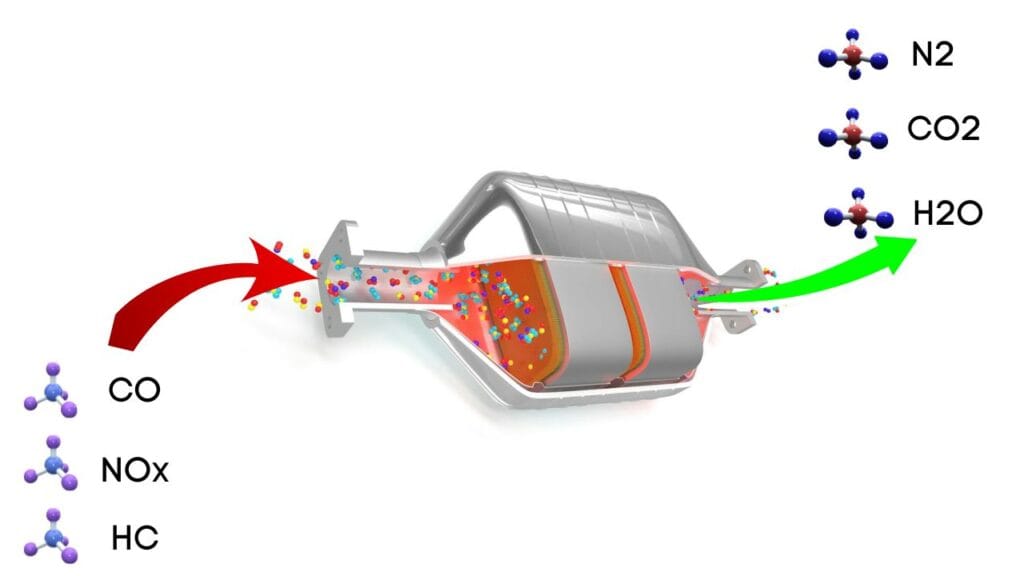
This code gets triggered when the Engine Control Module detects a condition that indicates that the catalytic converter is operating below the minimum allowable efficiency threshold.
When Bank 1 Catalytic converter efficiency below threshold— the ECM flags it as a problem and triggers the P0420 trouble code.
Read our free complete guide on Kindle and learn how to diagnose sensor-related issues with clarity and confidence.
STOP GUESSING. START DIAGNOSING. SAVE HUNDREDS ON REPAIRS.
Tired of expensive repair bills and mechanics who “parts-cannon” your car without finding the real issue? The “Check Engine” light shouldn’t be a mystery. This guide puts professional-level diagnostics in your hands.
What is Bank 1-Catalytic Converter?
In engines with multiple cylinder banks, like V6 or V8 engines, you’ll have two sides or “banks” of cylinders. Bank 1 typically refers to the side of the engine where cylinder 1 is located, and Bank 2 is on the opposite side.
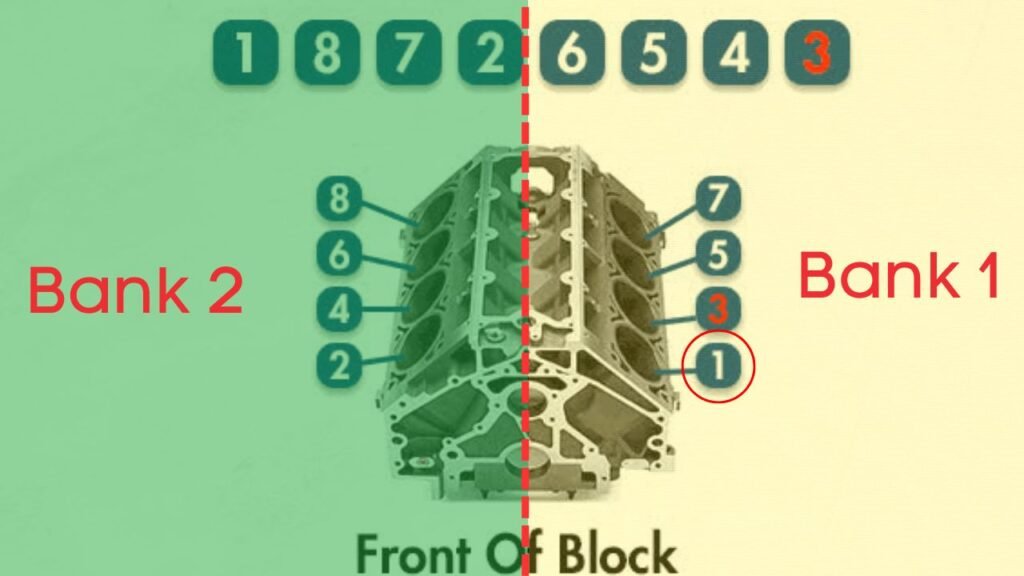

Each bank has its own exhaust line, and each exhaust line is equipped with a catalytic converter.
So, when we talk about bank 1 catalytic converter, we are focusing on catalytic converter specifically attached to the Bank 1 exhaust line.
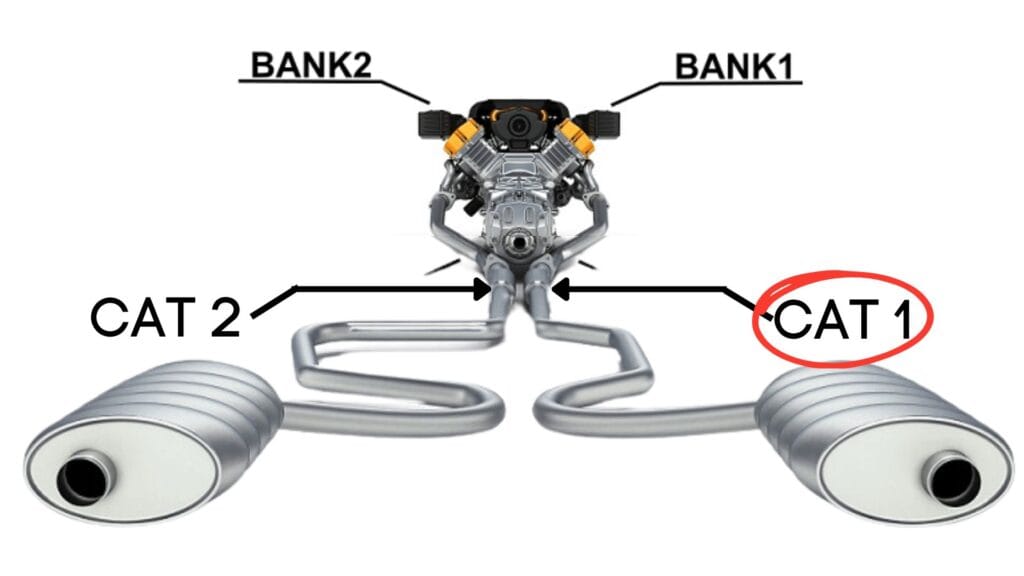

When the P0420 Triggers?
The catalytic converter’s job is to reduce harmful gases like carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. To ensure it’s working correctly, the oxygen sensors monitor the oxygen levels in the exhaust gases.
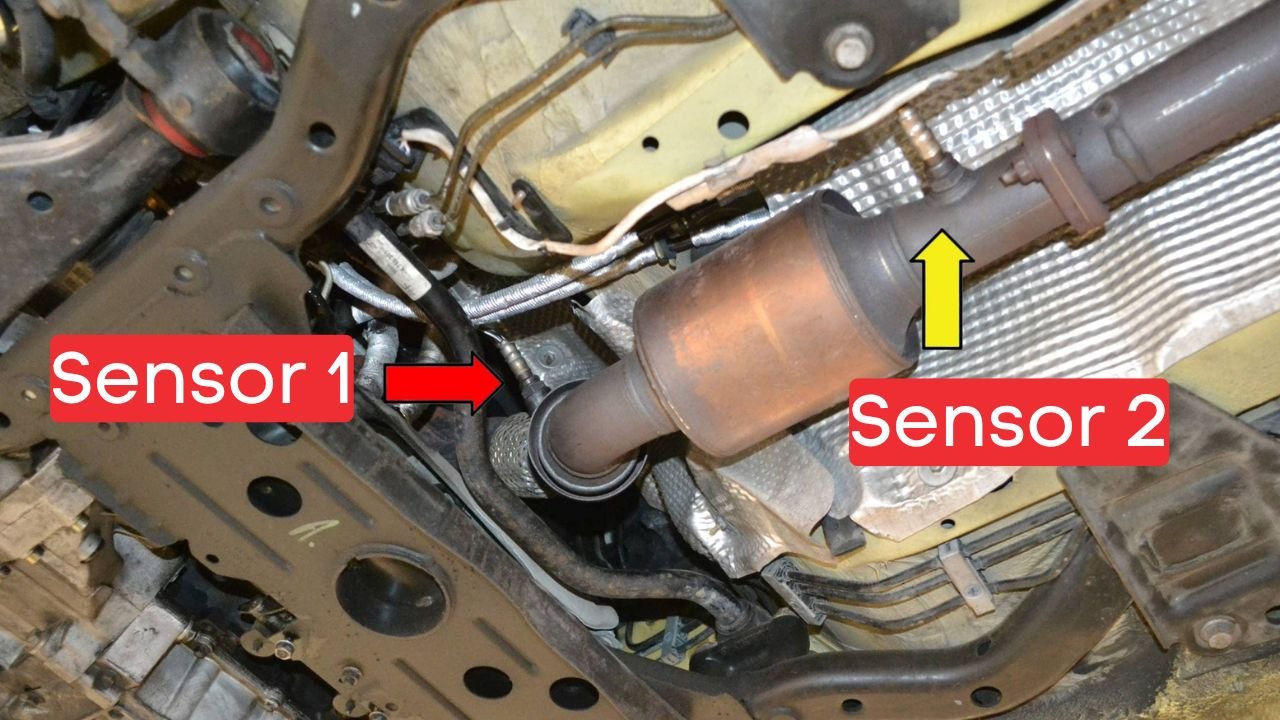
The catalytic converter has two oxygen sensors: one located upstream before the converter and one downstream after it. The ECU compares the readings from the upstream and downstream oxygen sensors.
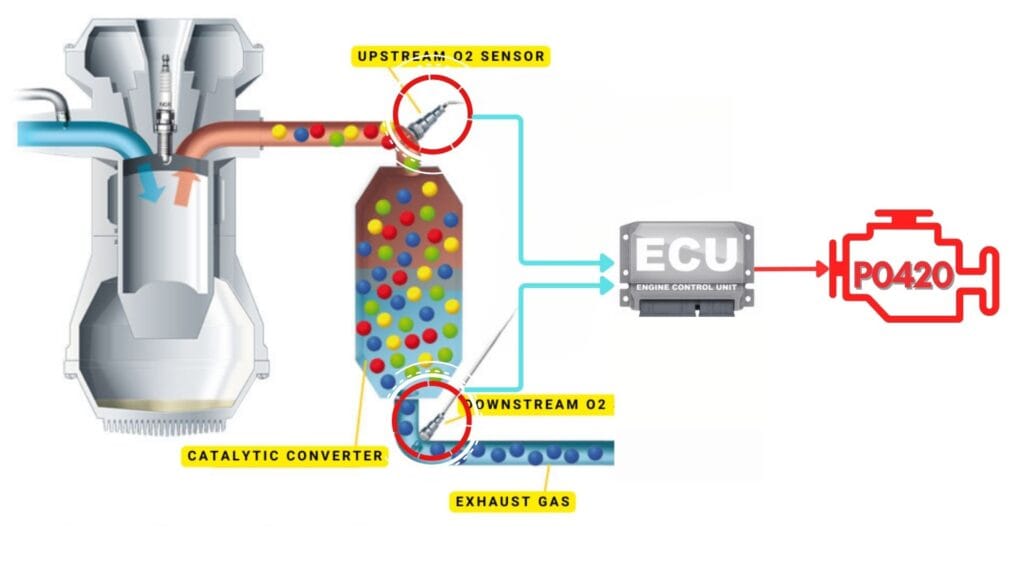

If the catalytic converter is functioning properly, the downstream sensor should show significantly lower oxygen content compared to the upstream sensor.
The P0420 code is triggered when the ECU detects that both upstream and downstream oxygen sensors are showing similar readings.
Read more about:
Car Sensors Explained: What They Do and How to Diagnose Them
With the increasing use of electronic systems in modern vehicles,…
Where is the P0420 Sensor or Oxygen Sensor Located?
Catalytic converters typically resemble exhaust mufflers and are integrated into the exhaust system upstream of the actual mufflers.
The oxygen sensors are strategically placed on either side of the catalytic converter. The upstream sensor is positioned before the catalytic converter, and the downstream sensor is located after the catalytic converter.

Read our free complete guide on Kindle and learn how to diagnose sensor-related issues with clarity and confidence.
STOP GUESSING. START DIAGNOSING. SAVE HUNDREDS ON REPAIRS.
Tired of expensive repair bills and mechanics who “parts-cannon” your car without finding the real issue? The “Check Engine” light shouldn’t be a mystery. This guide puts professional-level diagnostics in your hands.
How To Fix P0420?
Troubleshooting P0420 involves several steps, and we’ll discuss each one in detail. Let’s get started!
Before diving into specific repairs, perform an OBD-II scanner reset to clear the codes. Sometimes, these codes pop up due to recent maintenance work and can resolve themselves after a reset.
To reset the error codes, use an OBD-II scanner. Simply connect the scanner to your vehicle, follow the instructions to clear the trouble codes, and see if the P0420 code reappears.
If the code comes back, it means there’s a persistent issue that needs further troubleshooting.
Possible Root Causes of P0420
Some common root causes of the P0420 error code include:
1. Failed or Underperforming Catalytic Converter (Most Likely)
Over time, the catalytic converter can degrade, melt, or become contaminated, reducing its ability to convert harmful exhaust gases into less harmful emissions.
⚠️ Tip: Because catalytic converters are expensive to replace, it’s worth trying a catalytic converter cleaner first. Sometimes, carbon buildup can reduce efficiency, and a cleaner may help restore performance.
- Pass Emissions Tests with Confidence: Cataclean is specifically formulated to reduce carbon build-up and clean vital com…
- Enhance Fuel Economy and Performance: Cataclean cleans fuel injectors and cylinder heads, leading to improved fuel combu…
- Clear Check Engine Lights: By cleaning your car’s exhaust and fuel systems, Cataclean restores optimal performance and h…
2. Faulty Oxygen (O2) Sensor
A malfunctioning upstream or downstream O2 sensor can send incorrect signals to the ECM, making it believe the catalytic converter is underperforming.
Replacing a faulty oxygen sensor can sometimes clear the P0420 code if the converter itself is still in good condition.
- 【REPLACE#】15716, 15717, 15718, 15719, ZZC318861, XR3Z9G444CA, 15664, 234-4401, 234-4046. IF THE PLUG OF THE O2 SENSOR IS…
- 【REPLACEMENT FOR】2003-2014 Ford E150 E250 | 1999-2016 Ford E350 Super Duty | 2001-2010 Ford Escape | 1997-2011 Ford Expe…
- 【12-MONTH WARRANTY】If for any reason at all, you are not fully satisfied with the upstream downstream oxygen sensor, sim…
3. Damaged or Improperly Connected O2 Sensor Wiring.
Broken, corroded, or loose wiring can interrupt communication between the sensor and the ECM, leading to inaccurate readings.
You can test the continuity of oxygen sensor wiring using a digital multimeter to confirm if wiring is intact.
- Additional Tips – The following incorrect operations may cause the multimeter not to show results: Firstly, the plugs of…
- Versatile Digital Multimeter – Accurately measures AC/DC Voltage, DC Current, Resistance, and Diode. This Multimeter is …
- Troubleshooting with Accuracy – This Multimeter has a sampling speed of 2 times per second; Built-in a backlight LCD dis…
4. Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor Malfunction.
Incorrect coolant temperature readings can cause the ECM to miscalculate the air-fuel ratio.
An overly rich mixture may send excess unburned hydrocarbons into the exhaust, lowering catalytic converter efficiency.
⚠️ Tip: Check if other OBD-II codes related to coolant temperature are present. Replacing a faulty coolant temperature sensor may clear P0420.
- Professional, premium aftermarket replacement
- Provides the performance and dependability you expect from ACDelco
- Manufactured to meet expectations for fit, form, and function
5. Leaking or Damaged Exhaust Components.
Cracks or leaks in the exhaust manifold, catalytic converter, muffler, or exhaust pipes can cause false sensor readings.
Check visually for leaks in the exhaust system. For small leaks, you can use MufflerSeal (an iron-reinforced paste) or similar products to seal joints and cracks.
- J-B Weld Muffler Seal: MufflerSeal is an iron reinforced paste designed to seal mufflers, pipe joints and exhaust system…
- Cure Process: MufflerSeal can cure in two ways: By allowing the product to fully harden after it has been applied which …
- Projects: Mufflers, Pipe Joints and Exhaust Systems.
6. Retarded Spark Timing
Delayed ignition timing can increase emissions and reduce the effectiveness of the catalytic converter.
Sometimes, a weak spark leads to delayed combustion, leaving unburned fuel in the exhaust system. This excess fuel reduces catalytic converter effectiveness and can trigger code P0420.
In such cases, replacing worn spark plugs (or ignition coils if needed) often solves the issue.
- Designed specifically for the performance enthusiast, Iridium IX offers extreme ignitability, improved throttle response
- The 0.6 millimeter laser welded fine Iridium tip ensures high durability and a consistently stable spark and the tapered…
- Longer insulator , the corrugated ribs on insulator prevents flashover, and a triple gasket seal eliminates combustion g…
7. Leaking Fuel Injector or High Fuel Pressure
A leaking fuel injector may deliver more fuel than required, or excessive fuel pressure can push too much fuel into the cylinders. This excess fuel can overwhelm the catalytic converter, reducing its efficiency or causing permanent damage.
Inspect the fuel injectors and fuel pressure regulator. Replace a faulty injector or regulator as needed.
- 【ATTENTION】- Please enter your vehicle model in the “Amazon confirmed fit” plugin before purchasing these fuel injectors…
- 【Fitments 1】- Compatible With Chevy: SSR 5.3L 2003-2004 , Avalanche 1500 5.3L 2002-2004 , Tahoe 4.8L/5.3L 2000-2006 , Tr…
- 【Fitments 2】- Compatible With GMC : Yukon 4.8L 2000-2006 , Yukon 5.3L 2000-2006 , Yukon 6.0L 2001-2006 , Yukon XL 1500 5…
8. Cylinder Misfire
Misfires introduce unburned fuel into the exhaust, which can damage the catalytic converter.
Possible Solutions for P0420 Code
Possible solutions include:
- Inspect for Exhaust Leaks:
- Check the exhaust manifold, pipes, catalytic converter, and connections for leaks or damage. Repair or replace as needed.
- Diagnose Oxygen Sensor Operation:
- Use an oscilloscope or diagnostic scanner to check the oxygen sensor’s operation.
- Upstream Sensor (Before Catalytic Converter): Should display a fluctuating waveform due to variations in air-fuel mixture.
- Downstream Sensor (After Catalytic Converter): Should have a more steady waveform if the catalytic converter is functioning correctly.
- Test and Replace the Downstream Oxygen Sensor:
- Inspect the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) behind the catalytic converter. Replace if faulty or damaged.
- Replace the Catalytic Converter (If Necessary):
- If the catalytic converter has failed or is no longer reducing emissions efficiently, replace it with an OEM or high-quality equivalent part.
- Check Fuel System Components:
- Inspect for leaking fuel injectors or high fuel pressure that may overwhelm the catalytic converter.
- Address any related fuel system issues before replacing major components.
- Inspect Spark Timing and Misfires:
- Check for retarded spark timing or cylinder misfires that could introduce unburned fuel into the exhaust system. Resolve any ignition system issues.
- Update PCM Software (If Applicable):
- In rare cases, the PCM may require a software update to correct false P0420 triggers. Check with the vehicle manufacturer for TSBs (Technical Service Bulletins).
Symptoms of the P0420 Code
Symptoms associated with P0420 can include:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: The most common indicator, often accompanied by stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Failed Emissions Test: The vehicle may fail an emissions test due to the catalytic converter’s inability to effectively reduce harmful pollutants.
- Rotten Egg Smell from the Exhaust: A strong sulfuric or “rotten egg” odor may be noticeable from the exhaust, indicating inefficient catalytic converter operation or unburned fuel in the exhaust.
- Reduced Engine Power Output: The engine may experience a noticeable drop in power, particularly during acceleration or while climbing hills.
- Inability to Accelerate: The vehicle may struggle to accelerate properly due to the catalytic converter becoming clogged or inefficient.
What does OBD2 code P0420 mean?
P0420 indicates that the catalytic converter on Bank 1 is not operating efficiently. The engine control module has detected that catalyst efficiency is below the expected threshold.
What are the most common causes of code P0420?
Common causes of P0420 include a failing catalytic converter, faulty oxygen sensors, damaged oxygen sensor wiring, exhaust leaks, engine misfires, incorrect air-fuel mixture, or engine coolant temperature sensor issues.
Can a bad oxygen sensor cause P0420?
Yes. A faulty upstream or downstream oxygen sensor, or damaged sensor wiring, can provide incorrect feedback to the engine control module and trigger a P0420 code.
Is it safe to drive with a P0420 code?
In many cases the vehicle may still be drivable, but prolonged driving with a P0420 code can lead to increased emissions, reduced fuel efficiency, and potential engine or exhaust damage.









Excellent information for a novice on any vehicle troubles. I feel confident going into the repair shop knowing I know as much as the technician does 😉 Thank you for the important assistance.
Glad, it helps you.
Thank you
Good job on explaining this code
Thanks
I appreciate your clear explanation of the systems function and component function and diagnostic information. Thank you, things do not need to be complicated.