P0114 Code Explained: Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Intermittent – Causes & Fixes
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. See our affiliate disclaimer for more information.
What does the P0114 Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit Intermittent mean?

The P0114 trouble code is a generic powertrain OBD-II diagnostic trouble code (DTC) that indicates an Intermittent Problem in the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor circuit.
When this code is stored, it means the Engine Control Module (ECM/ECU) has detected an electrical fault—such as an open circuit, short, or abnormal signal—in the IAT sensor circuit.
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the engine and sends this information to the ECU.
The ECU uses IAT data to adjust:
- Fuel delivery
- Ignition timing
- Air–fuel ratio
This is critical because:
- Cooler air is denser and contains more oxygen, requiring more fuel
- Warmer air is less dense, requiring less fuel
Accurate IAT readings help the engine maintain smooth operation, optimal performance, and fuel efficiency under all driving conditions.
The location of the IAT sensor depends on the vehicle design:
Most Modern Vehicles
- The IAT sensor is built into the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor
- Mounted in the air intake tube
- Typically located between the air filter box and the throttle body
Vehicles With a Standalone IAT Sensor
- Mounted on the plastic or rubber intake tube after the air filter
- Some engines have it threaded directly into the intake manifold
- Older models may place it inside or on the air filter housing
When the ECM detects that the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor signal becomes intermittent, it triggers the P0114 trouble code. The term intermittent indicates that the fault occurs sporadically or unpredictably, meaning the IAT signal may operate normally at times and then suddenly drop out, spike, or fluctuate without a consistent pattern.
Comparison Between P0110, P0111, P0112, P0113 and P0114
The P0110 code indicates an IAT sensor circuit malfunction, meaning the ECM has detected an electrical problem such as an open circuit, short to ground, short to voltage, or loss of reference voltage. The sensor signal may be missing or completely invalid.
The P0111 code refers to an IAT sensor range or performance problem. In this case, the sensor is electrically connected and sending data, but the temperature reading is implausible or does not change logically with engine and ambient conditions.
The P0112 code indicates an IAT sensor circuit low input condition. This occurs when the ECM detects a voltage signal that is lower than expected, typically representing an unrealistically cold intake air temperature caused by a short to ground or excessive resistance.
The P0113 code indicates an IAT sensor circuit high input condition. This happens when the voltage signal is higher than expected, usually due to an open circuit, disconnected sensor, broken wiring, or loss of ground, resulting in an unrealistically hot temperature reading.
The P0114 code indicates an intermittent IAT sensor signal. This means the signal drops out, spikes, or fluctuates unpredictably due to loose connections, wiring damage, vibration-related faults, or internal sensor failure.
Read our free complete guide on Kindle and learn how to diagnose sensor-related issues with clarity and confidence.
STOP GUESSING. START DIAGNOSING. SAVE HUNDREDS ON REPAIRS.
Tired of expensive repair bills and mechanics who “parts-cannon” your car without finding the real issue? The “Check Engine” light shouldn’t be a mystery. This guide puts professional-level diagnostics in your hands.
When the P0114 Triggers?
For the fuel injection system to operate correctly, the Engine Control Module (ECM) or Powertrain Control Module (PCM) must know the density of the air entering the engine. Air density directly affects how much fuel is required for efficient combustion—and air density is directly related to air temperature.
Because of this relationship, accurate intake air temperature data is essential for proper engine operation.
The Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor functions as a thermistor, meaning its electrical resistance changes as air temperature changes.
- Cold air → higher resistance → higher signal voltage
- Warm air → lower resistance → lower signal voltage
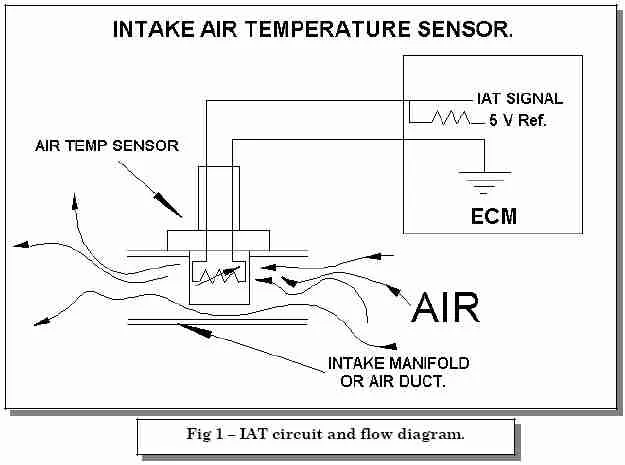

This changing voltage signal is sent to the ECU, which uses it to continuously adjust:
- Fuel delivery
- Ignition timing
- Air–fuel ratio
Since colder, denser air contains more oxygen, the ECU commands more fuel. Warmer, less dense air requires less fuel. This real-time adjustment allows the engine to run efficiently under varying temperatures and driving conditions.
When the ECM detects that the IAT sensor signal is intermittent, it triggers the P0114 trouble code.
In these cases, the ECM can no longer accurately calculate air density, forcing it to substitute default values and set the P0114 fault code.
Read more about:
Car Sensors Explained: What They Do and How to Diagnose Them
With the increasing use of electronic systems in modern vehicles,…
How To Fix P0114?
Troubleshooting P0114 involves several steps, and we’ll discuss each one in detail. Let’s get started!
Before diving into specific repairs, perform an OBD-II scanner reset to clear the codes. Sometimes, these codes pop up due to recent maintenance work and can resolve themselves after a reset.
Read our free complete guide on Kindle and learn how to diagnose sensor-related issues with clarity and confidence.
STOP GUESSING. START DIAGNOSING. SAVE HUNDREDS ON REPAIRS.
Tired of expensive repair bills and mechanics who “parts-cannon” your car without finding the real issue? The “Check Engine” light shouldn’t be a mystery. This guide puts professional-level diagnostics in your hands.
To reset the error codes, use an OBD-II scanner. Simply connect the scanner to your vehicle, follow the instructions to clear the trouble codes, and see if the P0114 code reappears.
If the code comes back, it means there’s a persistent issue that needs further troubleshooting.
Possible Root Causes of P0114
Some common root causes of the P0114 error code include:
1. Dirt Build-Up on the IAT Sensor Wire or Filament
This is one of the most frequent causes of the P0114 code, especially on vehicles where the IAT sensor is integrated into the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
Over time, dust, oil vapors, and debris from the intake air can accumulate on the IAT sensor’s sensing element or wire. When this buildup occurs, the sensor can no longer accurately measure the temperature of the incoming air.
Fix: In many cases, simply cleaning the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor is enough to resolve the P0113 code. However, it is important that the sensor is cleaned correctly. Only a dedicated IAT or MAF sensor cleaner should be used, as it is specifically designed to be fast-evaporating and completely residue-free. Using brake cleaner, carburetor cleaner, or compressed air can permanently damage the delicate sensing element. The sensor element should never be touched with fingers, tools, or cloths, as even slight physical contact can alter its calibration.
- Increases Horsepower And Improves Air/Fuel Ratio And Mpg
- Plastic Safe-Dries In Seconds
- Not Voc Compliant For California & Otc
2. Open or Shorted Wiring in the IAT Circuit
Another common cause of the P0114 code is an open or shorted circuit in the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor wiring. The IAT sensor relies on a stable reference voltage and a clean ground circuit to send an accurate temperature signal to the ECM. If either the signal wire or ground wire becomes damaged, the sensor’s voltage output will fall outside the expected range.
Wiring faults often occur due to heat exposure near the engine, vibration, or physical damage along the intake tract. Chafed insulation, broken wires inside the harness, corrosion in connectors, or loose terminal pins can interrupt the electrical signal. In some cases, the signal wire may short to ground or to battery voltage, causing the ECM to detect an implausible reading or no signal at all.
When the ECM sees a constant high or low voltage that does not change with intake air temperature, it interprets this as a circuit malfunction rather than a normal sensor error. As a result, it stores the P0114 trouble code.
Fix: To fix wiring-related IAT circuit issues, carefully inspect the wiring harness and electrical connectors for visible signs of wear, fraying, heat damage, or corrosion. Pay close attention to areas near the intake system and engine components where vibration and heat are most likely to cause damage. Use a digital multimeter (DMM) to check circuit continuity, verify the presence of the correct reference voltage, and confirm a solid ground connection. If any damaged wires, loose terminals, or corroded connectors are found, repair or replace them as necessary to restore proper signal flow and clear the P0114 code.
- Additional Tips – The following incorrect operations may cause the multimeter not to show results: Firstly, the plugs of…
- Versatile Digital Multimeter – Accurately measures AC/DC Voltage, DC Current, Resistance, and Diode. This Multimeter is …
- Troubleshooting with Accuracy – This Multimeter has a sampling speed of 2 times per second; Built-in a backlight LCD dis…
3. Faulty IAT Sensor
A failed Intake Air Temperature (IAT) sensor itself is another common cause of the P0114 trouble code. Over time, the internal thermistor can degrade, crack, or lose its ability to change resistance accurately in response to temperature changes. When this happens, the sensor may become stuck at a fixed resistance value or produce an erratic voltage signal that no longer reflects actual intake air temperature.
In many cases, a failed IAT sensor will report implausible temperature readings, such as extremely cold or extremely hot values that do not match ambient conditions or engine operating state. If the ECM detects that the IAT signal is outside the expected electrical range, does not respond to temperature changes, or conflicts with data from related sensors like the coolant temperature sensor, it will identify the fault as a circuit malfunction and trigger the P0114 code.
Fix: If cleaning the IAT sensor does not resolve the issue, the next step is to test the sensor using a digital multimeter or an OBD-II scan tool. Resistance values or live intake air temperature data should be checked and compared against the manufacturer’s specifications. If the sensor readings are incorrect, erratic, or outside the specified range, the IAT sensor should be replaced. Using a high-quality OEM or OEM-equivalent replacement is strongly recommended to ensure accurate temperature measurement and prevent repeat P0114 faults.
- Package Included: 1 x Intake Air Temperature Sensor, 1 x Pigtail Harness as pictured.
- Replace OE Part Number: 25036751, 25037225, 25037334, 25037034, 213-192, 213-190, 54001, 12124075, 15335987, 15317832, 1…
- Compatible With: Fits For GM (Buick/Cadillac/Chevrolet/GMC/Pontiac/Oldsmobile) and more.