P0172: System too Rich (Bank 1)
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. See our affiliate disclaimer for more information.
What does the P0172 System too Rich (Bank 1) mean?
P0172 code gets triggered when the Engine Control Module receives an input signal from the oxygen sensor—also called the air-fuel ratio sensor—indicating that the air/fuel mixture has been running too rich for an extended period of time.
Now, let’s talk specifics. A rich mixture means insufficient air and too much fuel in the combustion process, which can lead to poor engine performance, increased emissions, and potential damage over time.
When this happens on Bank 1— the ECM flags it as a problem and triggers the P0172 trouble code.
Read our free complete guide on Kindle and learn how to diagnose sensor-related issues with clarity and confidence.
STOP GUESSING. START DIAGNOSING. SAVE HUNDREDS ON REPAIRS.
Tired of expensive repair bills and mechanics who “parts-cannon” your car without finding the real issue? The “Check Engine” light shouldn’t be a mystery. This guide puts professional-level diagnostics in your hands.
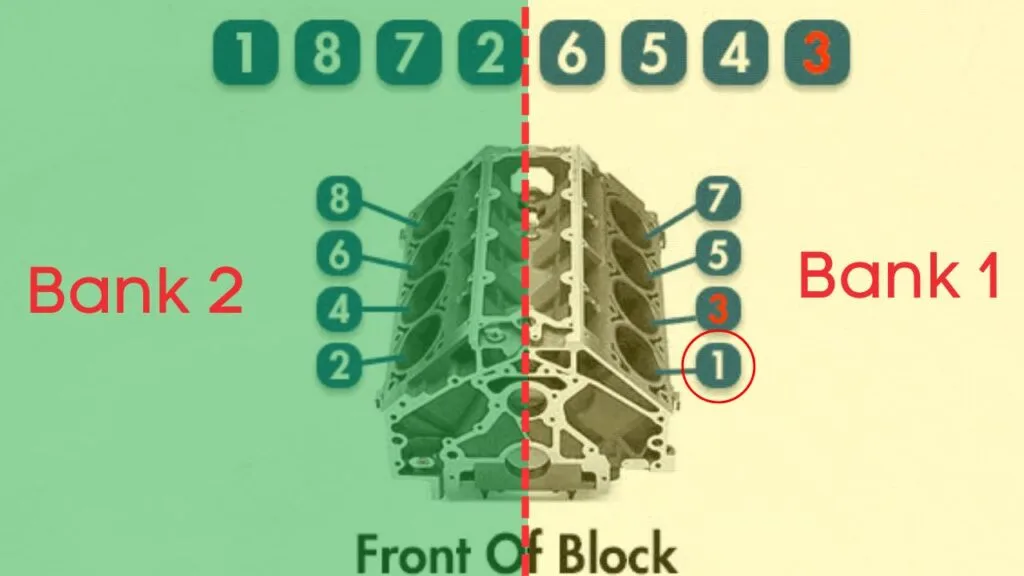
What is Bank 1?
In engines with multiple cylinder banks, like V6 or V8 engines, you’ll have two sides or “banks” of cylinders. Bank 1 typically refers to the side of the engine where cylinder 1 is located, and Bank 2 is on the opposite side.

When the P0172 Triggers?
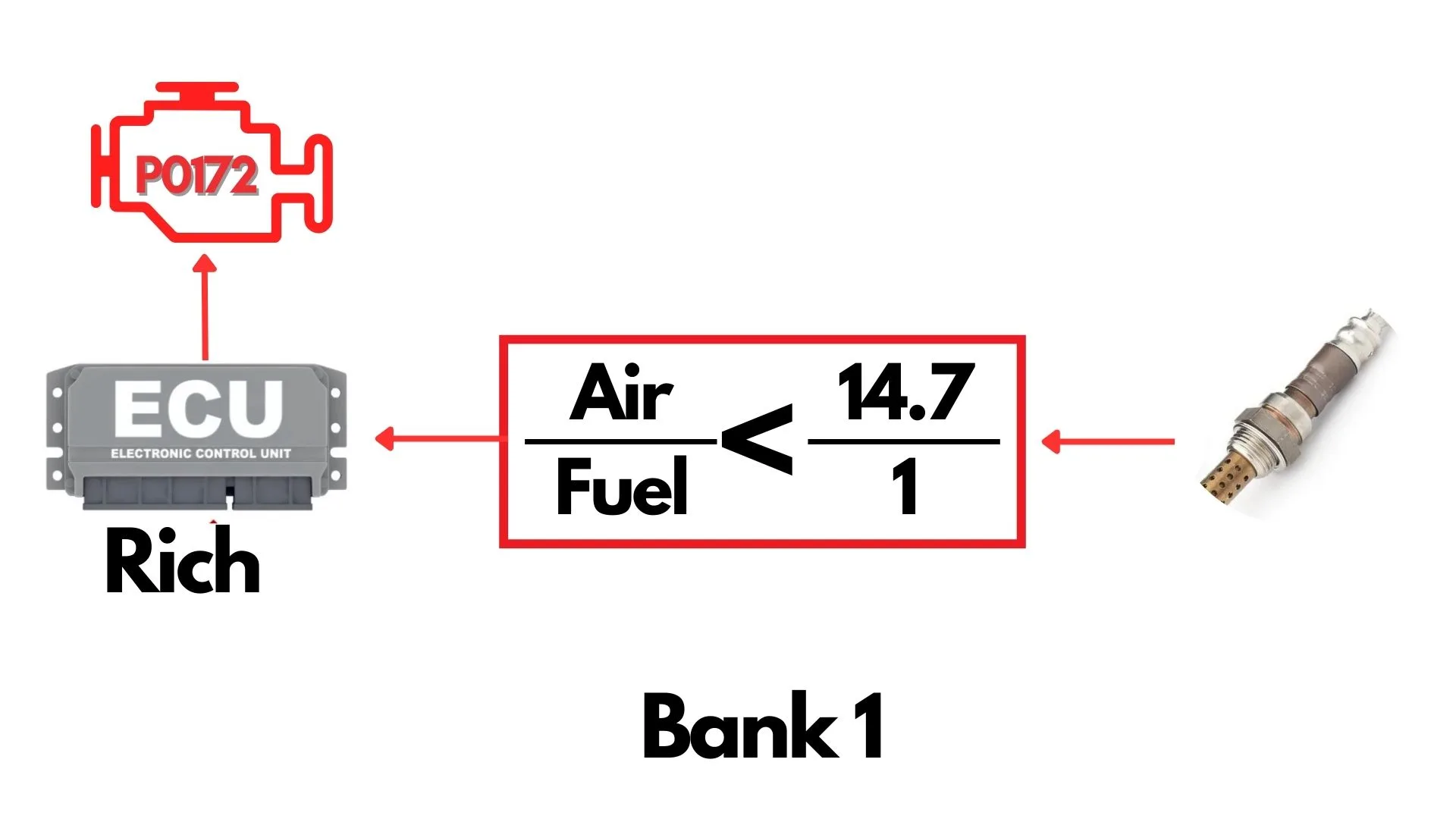
In a fully functional system, the upstream oxygen sensor, also called the air-fuel ratio sensor, measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases as they leave the engine. This real-time data helps the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) adjust the air-fuel mixture for optimal performance.
For gasoline engines, the ideal air-fuel ratio is 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel—this is known as the stoichiometric ratio. When the mixture is at this ratio, combustion is efficient, and emissions are minimized.
But when the oxygen sensor detects that the air-fuel ratio is lesser than 14.7:1—meaning there’s too little air or too much fuel in the mixture—the PCM interprets this as a ‘rich’ condition.
If this rich condition persists for extended period of time, the PCM triggers the P0172 code, indicating that the system on Bank 1 is running too rich.

Read more about:
Car Sensors Explained: What They Do and How to Diagnose Them
With the increasing use of electronic systems in modern vehicles,…
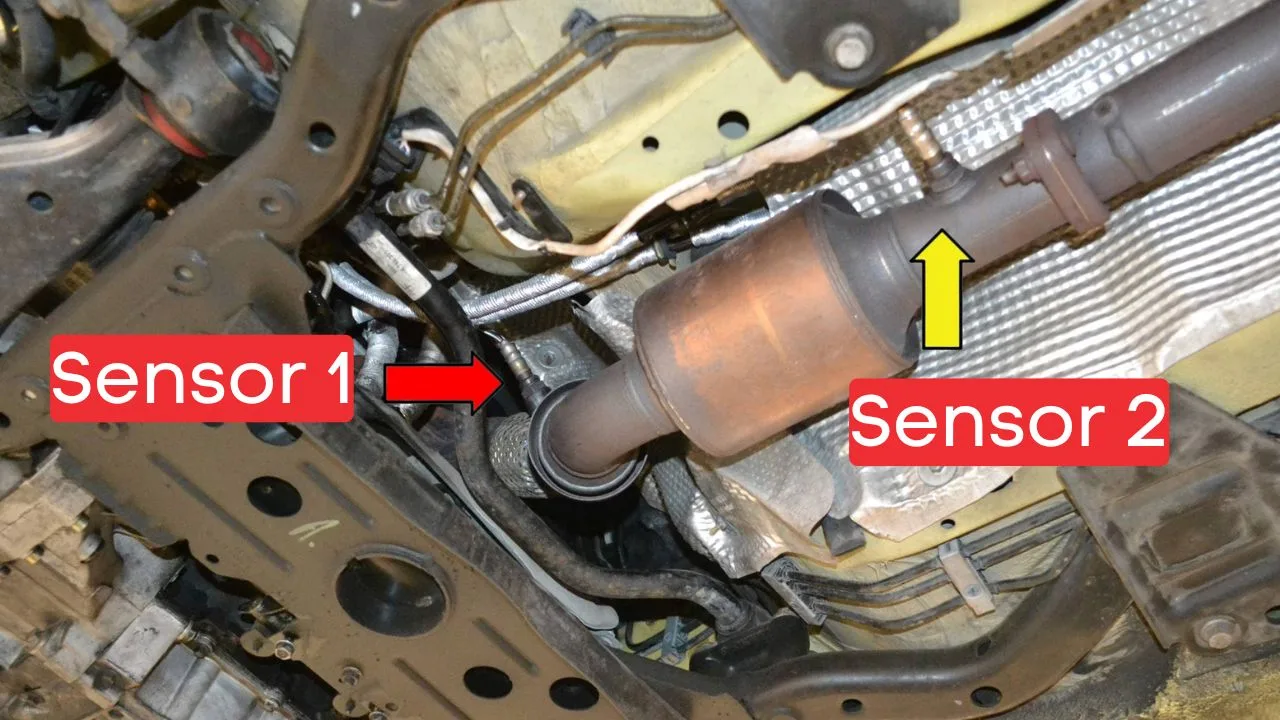
Where is the P0172 Sensor or Oxygen Sensor Located?
The P0172 sensor, also known as the Oxygen Sensor or Air-Fuel Ratio Sensor, is generally located in the exhaust system, upstream of the catalytic converter on Bank 1. This sensor position can vary slightly depending on your vehicle’s make and model, but it’s usually found near the exhaust manifold.

Read our free complete guide on Kindle and learn how to diagnose sensor-related issues with clarity and confidence.
STOP GUESSING. START DIAGNOSING. SAVE HUNDREDS ON REPAIRS.
Tired of expensive repair bills and mechanics who “parts-cannon” your car without finding the real issue? The “Check Engine” light shouldn’t be a mystery. This guide puts professional-level diagnostics in your hands.
How To Fix P0172?
Troubleshooting P0172 involves several steps, and we’ll discuss each one in detail. Let’s get started!
Before diving into specific repairs, perform an OBD-II scanner reset to clear the codes. Sometimes, these codes pop up due to recent maintenance work and can resolve themselves after a reset.
To reset the error codes, use an OBD-II scanner. Simply connect the scanner to your vehicle, follow the instructions to clear the trouble codes, and see if the P0172 code reappears.
If the code comes back, it means there’s a persistent issue that needs further troubleshooting.
Possible Root Causes of P0172
Some common root causes of the P0172 error code include:
1. Leaking Fuel Injector
A stuck-open or leaking fuel injector can allow more fuel than required to enter the combustion chamber. This results in a rich air-fuel mixture, which is one of the most common causes of the P0172 code. The excess fuel disrupts proper combustion, increases emissions, and can damage the catalytic converter over time.
Fix: Inspect the fuel injectors for leaks or clogging. Replace or clean them as necessary.
- [Vehicle Fitment-1]: Compatible with Ford Bronco 1990-1996 V8 5.0L, Bronco 1991-1996 V8 5.8L, Crown Victoria 1992-1997 V…
- [Vehicle Fitment-2]: Compatible with Ford E-150 Econoline Club Wagon 1990-1996 V8 5.8L, E-250 2003-2004 V8 4.6L, E-250 2…
- [Vehicle Fitment-3]: Compatible with Ford E-350 Super Duty 1999-1999 V8 5.4L, E-450 Econoline Super Duty 2000-2002 V8 5….
2. Faulty Fuel Pressure Regulator
A malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator or a restriction in the fuel return line can cause fuel rail pressure to become too high. This results in excessive fuel delivery to the injectors, creating a consistently rich air-fuel mixture. Over time, this condition can lead to poor fuel economy, carbon buildup, and trigger the P0172 code.
Fix: Test the fuel pressure with a gauge. If readings are above specifications, inspect the fuel pressure regulator and return line. Replace the regulator if faulty.
- PRECISION EFI FUEL PRESSURE CONTROL: This adjustable fuel pressure regulator for electric fuel injection return line sys…
- COMPACT RETURN LINE REGULATOR LAYOUT: Two ORB-06 inlet ports and one ORB-06 return port support clean fuel hose and line…
- BUILT FOR MONITORING AND TUNING: Includes a dedicated 1/8″ NPT port for attaching a fuel pressure gauge, allowing for ac…
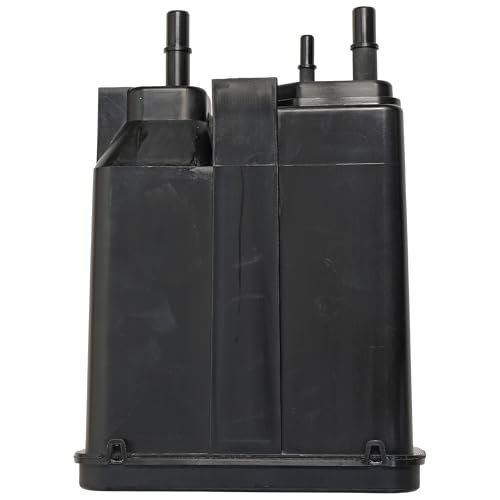
3. Saturated Charcoal Canister
The EVAP charcoal canister stores excess fuel vapors and routes them back into the intake through the purge valve. If the fuel tank is frequently overfilled, the charcoal canister can become saturated with liquid fuel. This leads to unregulated fuel vapors entering the intake manifold, enriching the air-fuel mixture and potentially triggering the P0172 code.
Fix: Inspect the EVAP system for raw fuel contamination. If the canister is saturated, replace it and avoid topping off the fuel tank after the pump shuts off.
- Application: Evap Canister Charcoal Canister for 2004-2020 Chevy Silverado 1500 2500 3500 HD Classic Express 1500 2500 3…
- Application: Evap Canister Charcoal Canister for 2004-2020 GMC Savana 1500 2500 3500 Sierra 1500 2500 3500 HD Classic
- Application: Evap Canister Charcoal Canister for 2004-2005 Workhorse FasTrack FT1261 FT1061 FT1461 FT1601 FT1801
4. Clogged Air Filter
A clogged or excessively dirty air filter restricts airflow into the engine. With less air entering the combustion chamber, the ECU continues injecting the same amount of fuel, resulting in an overly rich air-fuel mixture. Over time, this imbalance can trigger the P0172 code.
Fix: Inspect and replace the air filter at regular intervals. Using a high-quality or OEM-recommended air filter helps maintain proper airflow.
- ENGINEERED POWER – Designed to increase horsepower and acceleration. Clogged or dirty air filters can reduce your vehicl…
- ECO FRIENDLY – Washable and reusable air filter helps reduce replacement waste, which last longer than 10 disposable fil…
- EASY INSTALLATION – Pre-oiled and built with simple clamp-on design, it is one of the easiest and most cost-effective up…
5. Restrictions in the Air Intake System
Any blockages or restrictions in the intake system—such as clogged ducts, a dirty throttle body, or debris in the air passages—can limit airflow. Reduced airflow causes the ECU to inject more fuel than necessary, creating an overly rich air-fuel mixture and triggering the P0172 code.
Fix: Inspect the entire air intake system. Clean the throttle body and intake passages using a jet spray cleaner to restore proper airflow.
- The information below is per-pack only
- Helps Overcome Hard Starting, Rough Idling, Stalling, And High Exhaust Emissions
- Quickly Removes Deposits From The Inside And Outside Of The Carburetor To Improve Engine Performance And Fuel Economy
6. Faulty Oxygen (O2) Sensor
While O2 sensors more commonly fail by falsely reading lean, this incorrect feedback can cause the ECU to adjust fuel delivery improperly, leading to a consistently rich mixture and triggering P0172.
Fix: Test the O2 sensor’s voltage response with a digital multimeter or scan tool. If faulty, replace the sensor.
- 【REPLACE#】15716, 15717, 15718, 15719, ZZC318861, XR3Z9G444CA, 15664, 234-4401, 234-4046. IF THE PLUG OF THE O2 SENSOR IS…
- 【REPLACEMENT FOR】2003-2014 Ford E150 E250 | 1999-2016 Ford E350 Super Duty | 2001-2010 Ford Escape | 1997-2011 Ford Expe…
- 【12-MONTH WARRANTY】If for any reason at all, you are not fully satisfied with the upstream downstream oxygen sensor, sim…
Symptoms of the P0172 Code
Symptoms associated with P0172 can include:
- Illuminated Check Engine Light: The most common indicator, often accompanied by stored diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs).
- Lack of Engine Power: The engine may feel sluggish or underpowered due to the overly rich air-fuel mixture disrupting combustion.
- Rough or Rolling Idle: The engine may idle inconsistently, causing noticeable vibrations or fluctuations in RPM.
- Hesitation on Acceleration: A delayed or unsteady response when pressing the accelerator, as excess fuel floods the combustion chamber.
- Misfiring: Cylinders may misfire due to incomplete combustion caused by the rich mixture.
- Strong Fuel Odor: An excessive fuel smell may emanate from the exhaust or even the vehicle’s cabin, indicating unburned fuel.
- Poor Fuel Economy: Increased fuel consumption as the engine burns more fuel than necessary.








With all that said. and knowing what has been serviced most recently. I would check what has not been serviced and that would be the spark plugs.
Thank you for such an informative post that is easy to understand .